Laser Welding: Innovation and Precision in Metal Fabrication
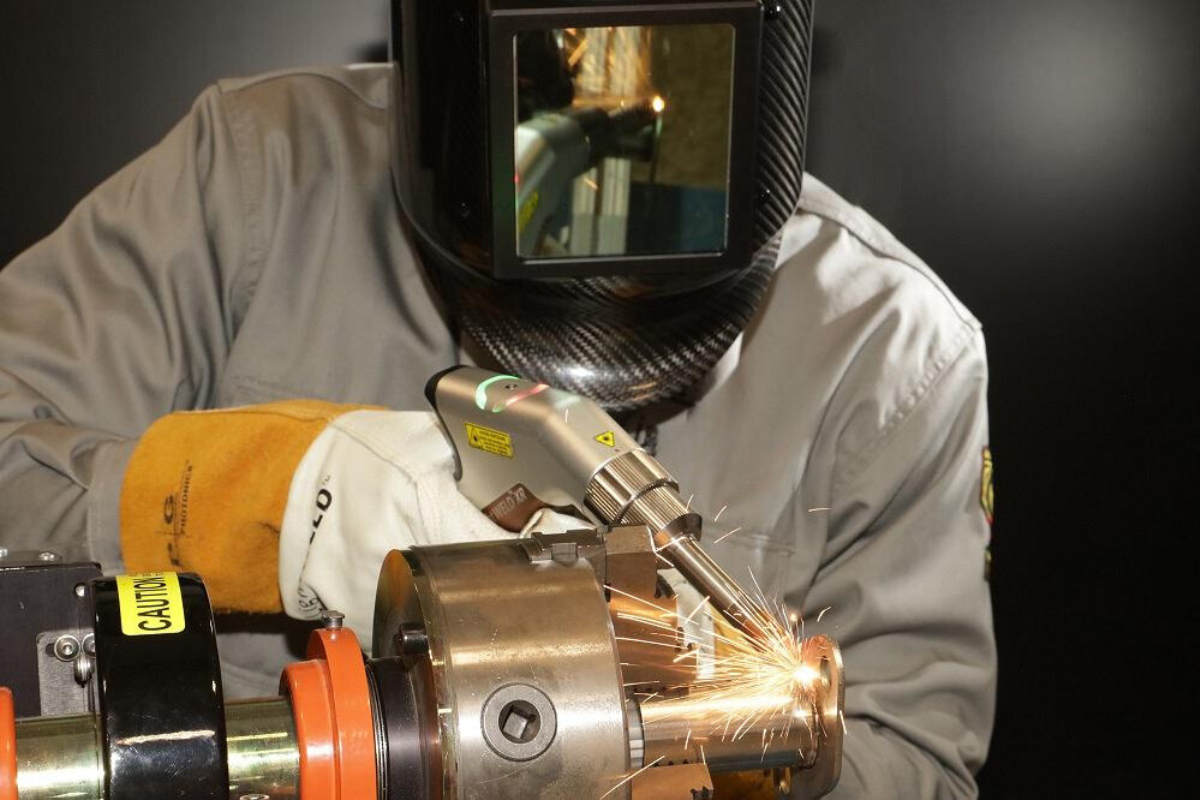

Laser welding has emerged as an advanced and highly precise technology in the field of metal fabrication. It combines the precise focusing capability of the laser beam with automated control, offering significant advantages over traditional welding methods in terms of speed, quality, and application possibilities. In this article, we will explore how laser welding works, its applications, advantages, limitations, and its impact on modern industry.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a process that uses a concentrated laser beam as a heat source to fuse materials, usually metals or thermoplastics. The laser, an acronym for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation,” is capable of generating a coherent, high-intensity beam of light that can be focused on an extremely small area. This allows the material to be quickly heated and melted at the point of focus, creating a precise and clean weld.
Mechanism of Action
The process begins when the laser beam focuses on the surface of the material. The laser energy is absorbed in the contact area, rapidly increasing the temperature until the material melts. In laser welding, two types of methods are generally used: heat conduction and deep-penetration welding.
1. Heat Conduction: In this method, the laser heats the surface without vaporizing the material, and the melt is spread by thermal conductivity. This technique is used for superficial joints where deep penetration is not required.
2. Deep Penetration: Here, the laser penetrates deeply creating a “keyhole” or gap that allows a total fusion along the joint. This type of weld is ideal for deeper joints and for applications that require high structural strength.
Process Control
Control of the laser welding process is critical to ensure joint quality and consistency. The most common parameters to monitor include laser power, feed rate, wavelength, and the type of shielding gas used (usually argon or helium) that protects the weld from oxygen and other impurities that could compromise the integrity of the material.
Advantages of Laser Welding
Laser welding offers numerous advantages over traditional welding techniques, including:
1. High Precision and Quality: The ability to focus the laser beam on very specific areas allows for extremely precise welds without damaging surrounding areas, making it ideal for applications where detail is crucial.
2. Speed and Efficiency: Due to the high energy concentration of the laser, the welding process is much faster than other methods. This not only reduces processing time but also improves energy efficiency.
3. Automation and Flexibility: Laser welding can be easily automated using CNC control systems and robotics, allowing a high degree of repeatability and precision, ideal for mass production.
4. Low Deformation: The laser’s high speed and precise focusing minimize the heat-affected zone, thus reducing thermal deformation in components.
5. Variety of Materials: Works with a wide range of materials, including stainless steels, carbon steels, titanium, aluminum, and exotic alloys. It is also suitable for metal combinations that are difficult to join with conventional methods.
Applications of Laser Welding
Laser welding is used in a wide range of industries due to its unique characteristics. Here are some notable applications:
1. Automotive Industry
Laser welding has become an essential technology in vehicle production. Applications include:
- Body Manufacturing: Laser welding allows the joining of body panels with high precision, forming light and resistant structures. This approach reduces the weight of the vehicle, which improves fuel efficiency and decreases CO2 emissions.
- Engine Components: Used to weld internal components such as engine housings, exhaust systems, and transmissions. Precise welding ensures a tight seal, which is crucial for mechanical performance.
2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, where safety and reliability are paramount, laser welding is used in:
- Engine Assemblies: Jet engine components, such as bushings and housings, require strong, high-quality joints. Laser welding minimizes the risk of failure under extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
- Fuselages: Welding aircraft fuselages allows for the creation of lightweight and aerodynamic structures. The laser’s precision prevents deformation and ensures a perfect fit.
3. Electronics
The electronics industry benefits greatly from laser welding.
- Connectors and Cables: This method is applied to solder electrical connectors, ensuring perfect contact and avoiding resistance problems or short circuits.
4. Medical Industry
Laser welding has found its place in the medical industry, where precision is crucial:
- Medical Devices: Used to manufacture implantable devices, such as pacemakers and prosthetics, where reliability and biocompatibility are essential. Laser welding makes it possible to join materials such as titanium and stainless steel without contaminants.
- Surgical Instruments: The manufacture of high-precision surgical instruments, such as scissors and forceps, benefits from laser welding, which ensures a clean finish and great durability.
5. Consumer Goods Manufacturing
Laser welding is applied in the production of consumer goods in a variety of ways:
- Household appliances: Used in the manufacture of products such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens, where strong and aesthetically pleasing joints are required. The ability to weld thin and critical parts improves the quality of the final product.
6. Renewable Energies
In the renewable energy sector, laser welding has significant applications:
- Solar Structures: Used to weld metal structures and components for solar parks.
- Wind Turbines: Laser welding is ideal for joining wind turbine components, where high strength and durability are required to withstand extreme conditions.
7. Transportation Industry
Laser welding is essential in the manufacture of transport vehicles:
- Trains and Trams: It is used to join structural components in the manufacture of trains and trams, where precision and strength are critical to the safety of public transport.
- Ships and Boats: In the naval industry, it is used to weld structures such as hulls and internal components, guaranteeing joints that resist environmental stress and water conditions.
At EMS Group, our team specializes in providing high-quality manufacturing services tailored to your unique requirements. Whether you need prototyping, CNC bending, welding or assembly. Contact us today to discuss your project.
At EMS Group, innovation and customer satisfaction are our priority!