Metal Forging

Forging is an essential manufacturing process that transforms metals by applying compressive forces, usually using a hammer or die. Throughout history, forging has evolved significantly to include various techniques adapted to modern industrial needs. EMS Group, renowned for its innovation and excellence, offers a full range of forging services including cold forging, hot former, micro-forging,… allowing its customers to access customized and optimized solutions for their specific projects.
What are the advantages of ordering forgings from EMS Group?
- Expand your production capacity.
- Consult with EMS Group engineers about your forging project to find efficient and economical solutions.
- EMS Group takes care of the entire process, from quotation to delivery, including quality control.
- A single point of contact makes project management easier, allowing you to focus on tasks that add more value.
Material Selection
We make forging parts in different materials:
- Carbon Steels: Carbon steels are valued for their optimal balance between strength and plasticity, making them an economical and effective choice for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Alloy Steels : Alloy steels offer additional advantages, such as increased hardness and toughness, making them suitable for high-performance demands and applications that require robust materials.
- Stainless Steels : These steels are renowned for their corrosion resistance, making them ideal for use in aggressive environments where contact with corrosive agents is frequent.
- Aluminum Alloys: Aluminum alloys are noted for their lightness and corrosion resistance, making them a popular choice in the aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction is crucial.
- Titanium Alloys: Known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, titanium alloys are preferred in sectors such as aerospace, medical, and high-performance automotive, ensuring efficiency and durability.
- Copper Alloys: Copper alloys, which include brass and bronze, are renowned for their excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for electrical components and plumbing applications.
- Nickel Alloys: Nickel alloys are valued for their exceptional heat and corrosion resistance properties, being critical in applications within chemical manufacturing and aerospace engineering.
- Magnesium Alloys: As the lightest structural metal, magnesium alloys are used in applications where weight reduction is critical, bringing significant benefits in the design of structures and components.
Types of Forging
Cold Forging
Cold forging is a method that molds metal at room temperature, benefiting from several particular aspects that make it attractive for specific applications.
Cold Forging Features
- Increased Material Strength: By working metal without heating it, the strength properties are preserved, which can even be increased due to deformation hardening.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Offers excellent dimensional control and smooth surface finishes, reducing or even eliminating the need for downstream finishing processes.
- Material Efficiency: Provides efficient use of material, reducing waste and optimizing resources.
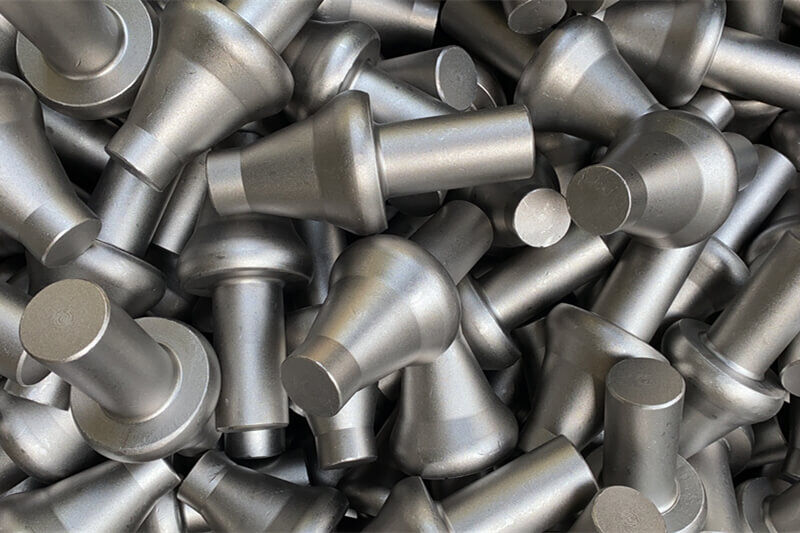

EMS Group implements cold forging to produce high-precision parts that require excellent surface finishes and increased strength, ideal for automotive components and high-demand electronics.
Hot Forging
This type of forging involves heating the metal to a temperature where it becomes ductile, allowing it to be manipulated into more complex shapes. It is widely used to manufacture large and heavy parts.
Hot Former Features
- Improved Formability: Allows for the processing of thicker and more complicated shaped materials without cracking.
- Reduced Forces: Less force is required to mold the metal, which can reduce tool wear and tear and cost less in energy inputs.
- Material Versatility: Allows working with high-strength alloys that would be difficult to forge in cold conditions.
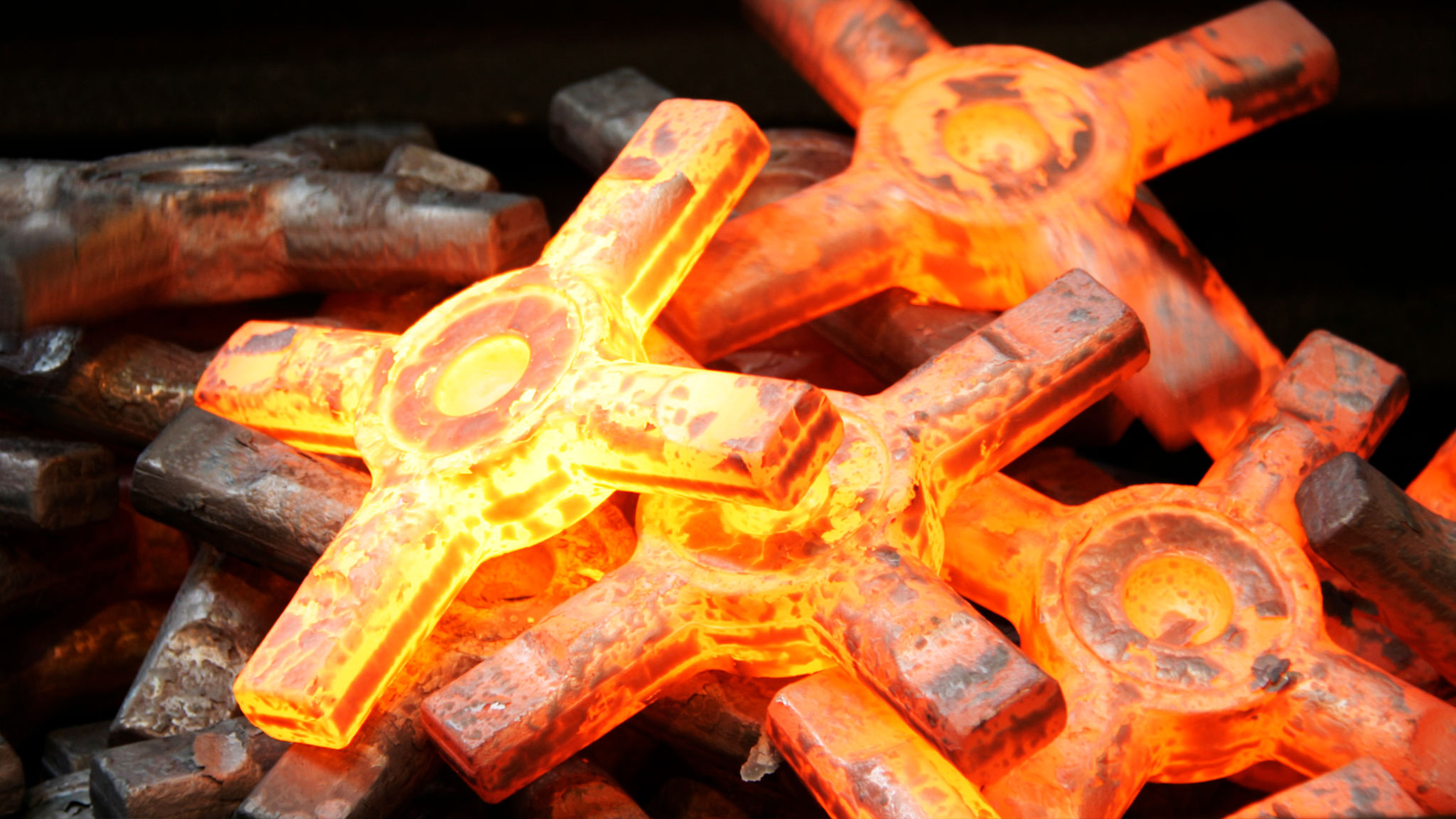

EMS Group maximizes the potential of hot forging for customers who need large, warp-resistant components, leveraging their ability to handle difficult materials efficiently and accurately.
Microforge
Microforging focuses on the production of very small parts with high precision, ideal for industries such as medical, microelectronics, and watchmaking.
Features of Microforging
- High Precision and Detail: Ability to create complex and detailed features in tiny parts.
- Rigorous Quality Control: Given the small size, the processes and finishes must be extremely precise.
- Specialized Materials: Use of materials that can adapt to small dimensions and maintain their functional properties.
EMS Group offers microforging as part of its commitment to providing advanced manufacturing solutions that adapt to current technological trends and demands.
Quality Control
Our quality control department performs robust quality control. EMS Group is ISO 9001 certified.
What is Metal Forging?
Metal forging is a fundamental industrial process that involves shaping metal by applying compressive forces. This method, which has been used for centuries, is crucial for the production of strong and durable parts, as deforming the metal at high temperatures improves its internal structure and increases its strength.
Despite its many advantages, forging presents certain challenges, such as the right choice of material, energy consumption during the process and accuracy in the final dimensions of the parts. These factors are critical to optimizing efficiency and quality in production.
Frequently asked questions about metal forging
How does the forging service work?
Once we prepare and open the mold or die for the forging process, we start mass production of forgings.
The steps of the forging process are as follows:
- Metal Heating: The metal is heated to high temperatures in a furnace or forge. This heating allows the metal to become malleable, facilitating its subsequent shaping.
- Metal Formation: Once hot, the metal is placed on an anvil or a forging die. Force is applied using a hammer or press to mold the metal into the desired shape.
- Reheating and Remodeling: The metal may need to be reheated and reformed several times during the process to achieve the required geometry and mechanical properties.
- Cooling and Hardening: After forming, the metal is cooled, which can be done by tempering it in water or oil, which helps to increase its hardness and strength.
Importantly, forged metal parts typically require additional processing, such as machining, heat treatment, or other methods, to reach the desired final properties and finishes.
Is it possible to use hot and cold forging together in a manufacturing process?
Yes, some manufacturing processes combine hot and cold forging to take advantage of each method. Hot forging is used to create the initial shape, followed by cold forging to improve the mechanical properties and finish of the component.
What is the difference between stamping forging and strain forging?
Stamping forging primarily involves cutting and shaping flat sheet metal with high precision, while strain forging focuses on reducing the diameter and creating specific profiles on cylindrical or tubular workpieces using radial compression.
With cutting-edge technologies and a dedicated team of specialists, EMS Group is ready to meet the present and future challenges of forging, always providing superior quality and customized solutions that exceed the expectations of its customers.