Sheet Metal Fabrication: Introduction to Key Techniques and Processes

Sheet metal fabrication is an essential element in modern production, considering its presence in multiple sectors, from the automotive industry to construction. Sheet metal working techniques make it possible to transform materials into final products that meet quality standards and structural specifications. In this article, we will explore the fundamental concepts related to sheet metal fabrication, as well as the most common techniques employed in the industry.
What is Sheet Metal?
Sheet metal is defined as a metal material that has been processed and cut to specific dimensions. It is generally produced in sheets of different thicknesses and has a variety of uses, from structural components to decorative elements. Sheet metal fabrication is based on techniques that allow this material to be shaped, cut, bent and assembled to create final products that meet various industrial applications.
Main Techniques in Sheet Metal Fabrication
1. Cutting
Cutting is the first step in sheet metal fabrication and can be done using several methods, including:
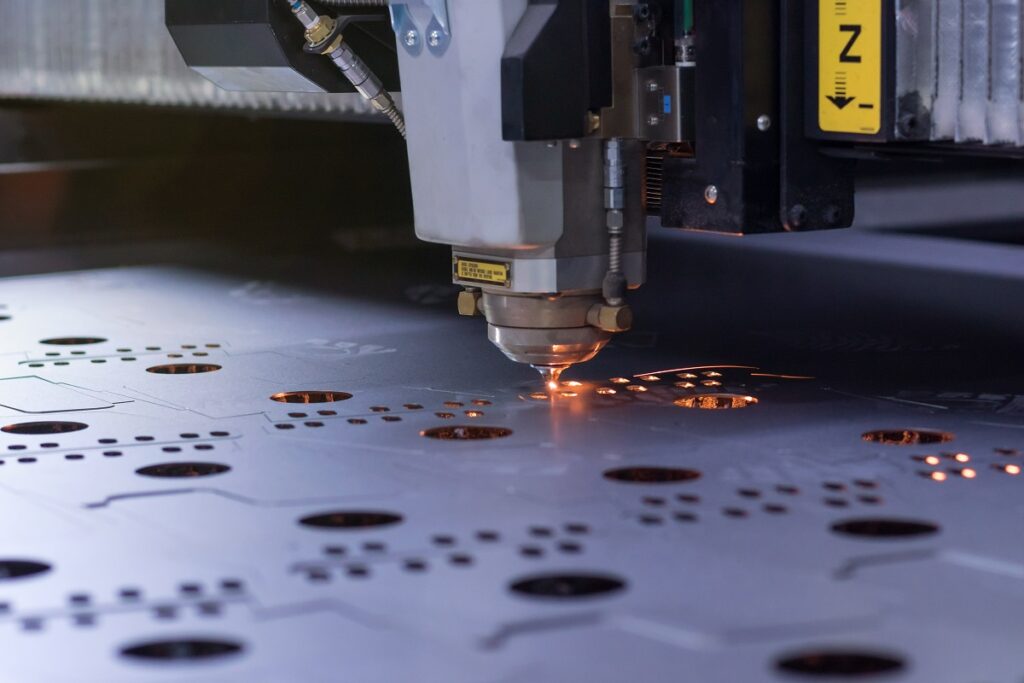
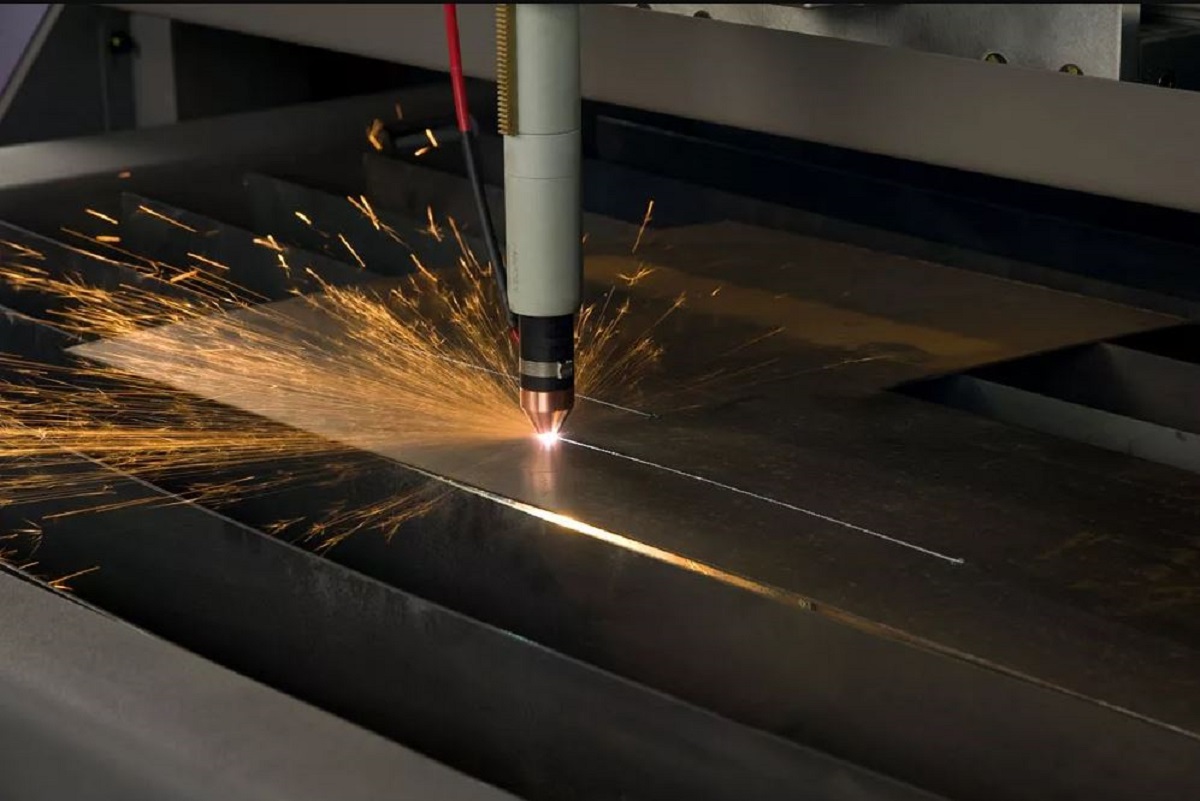
- Laser Cutting: This method uses a high-powered laser beam to make precise cuts in sheet metal.
There are three types of lasers used in laser cutting: CO2 (carbon dioxide), Nd (neodymium), and Nd-YAG (yttrium garnet and aluminum doped with neodymium impurities).
CO2 lasers have a high energy yield and a high output power ratio, and are used for cutting thin material, engraving, and drilling. Nd lasers have high energy but low repetition efficiency. They are used for engraving, drilling and welding.
Nd-YAG lasers have very high power and can cut thicker materials. However, it is more expensive to operate than CO2.
Laser cutters can work with aluminum, steel, copper, stainless steel, and other metals. They are best used to cut thin parts (with a maximum thickness of 15 mm for aluminum and 6 mm for steel), engraving and drilling.
The advantage of this process lies in its ability to make complex cuts with a minimum margin of error, in addition to its speed and energy efficiency.

- Waterjet Cutting: Uses a mixture of water and high-pressure abrasives to cut sheet metal. This method is especially useful for heat-sensitive materials and allows clean cuts to be achieved without altering the properties of the material.
Waterjet cutting can cut materials of varying thicknesses. The maximum thickness that can be cut depends on the material. Of all the CNC cutting methods, waterjet cutting is the most accurate, with tolerances ranging from 0.05 mm to 0.1 mm.
One of the reasons for its high precision is that, unlike its plasma and laser counterparts, waterjet cutting does not generate heat, so there is no heat-affected zone on the part.
Waterjet cutting is very versatile, as it is used to cut hard materials such as aluminum, steel, copper, stainless steel, and other metal alloys, as well as softer materials such as polymers, elastomers, wood, and foam.

- Plasma Cutting: Uses an electric arc to ionize the gas and create a jet of plasma that melts and cuts through sheet metal. It is an effective method for cutting thicker parts, although it can result in a less clean finish compared to laser cutting.
Plasma cutters can cut very thick materials, up to 300 mm for aluminum and 200 mm for steel, with a tolerance of 0.2 mm. Other materials that are processed with plasma cutters are stainless steel, copper and other metal alloys. Depending on the complexity of the part to be produced, 2 or 3-axis cutters can be used.
Although plasma cutters are not as diverse or precise as waterjet and laser cutters, they are the best choice for thick electrically conductive metal parts, as they are faster and more cost-effective for cutting these types of materials.

2. Folding
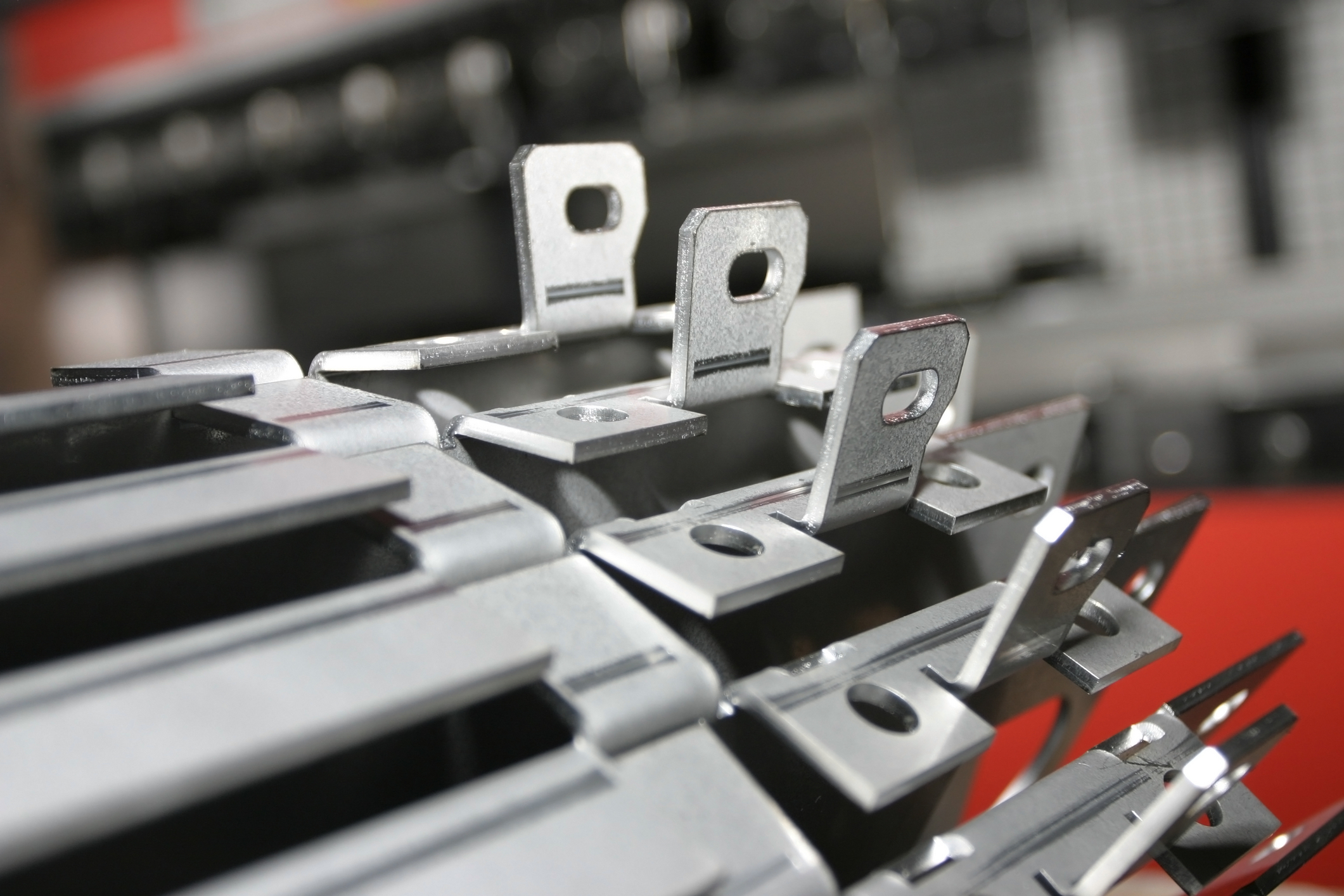
Bending is a process that involves shaping sheet metal by applying force to create angles and sections in the part. This process is carried out using bending presses, which can be manual or automated. Bending is essential in the manufacture of components such as boxes, brackets, and structures that require precise angular definitions.

3. Welding
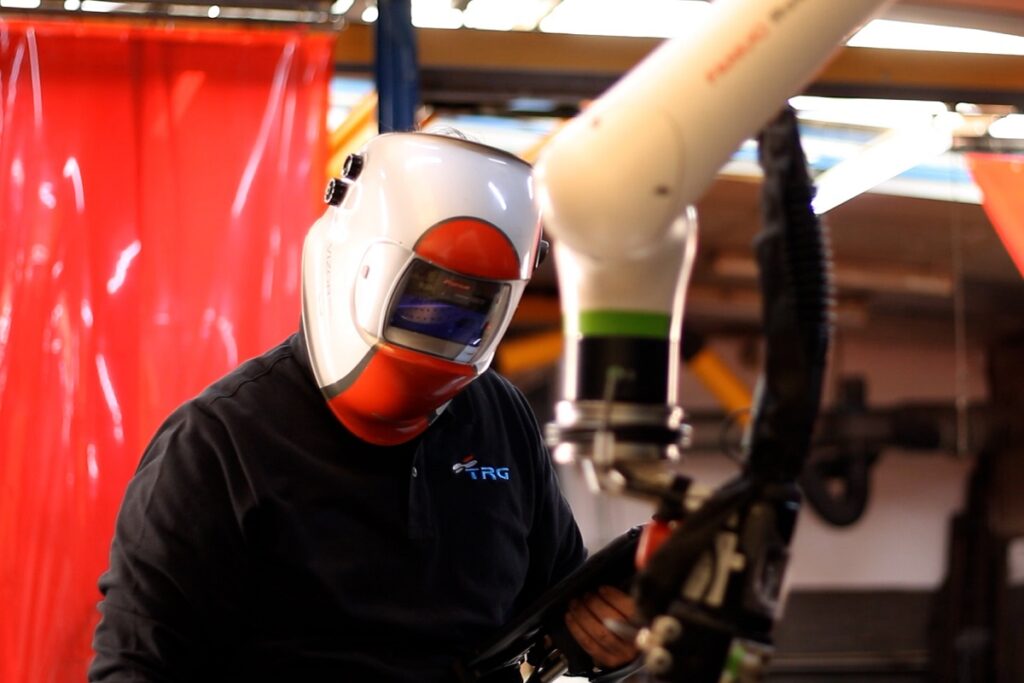
Welding is the process of joining metal parts together by applying heat, pressure, or both. There are different welding methods that can be used on sheet metal, such as:
- MIG MAG welding: It uses an electric arc and an inert gas to protect the molten metal. It is ideal for welding steel and aluminum, offering a clean and strong finish.
- TIG welding : Uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the arc. It is perfect for jobs that require high precision and control, such as welding stainless steel.
- Laser Welding : Laser welding for metal parts uses a highly concentrated laser light beam as a heat source to melt and fuse the edges of metal parts. This technique is known for its precision and high speed, allowing it to produce strong, high-quality joints with minimal thermal deformation.
- Resistance Welding : Resistance welding is a metal joining process that uses electrical resistance to the passage of a current to generate heat at the interface of the parts to be joined. When pressure and electricity are applied to metal parts, the heat generated by the material’s resistance melts the metal in the contact area, forming a solid bond as it cools.

Materials
The most suitable metals for this process are aluminum and its alloys, carbon steel, copper and its alloys, and stainless steel.
The most common finishes for sheet metal fabrication are blasting, anodizing, powder coating, and painting. In the case of warped or welded materials, heat treatment can be performed to relieve residual stresses.
Sheet Metal Applications
Sheet metal has a wide spectrum of applications in various industries, among which the following stand out:
- Automotive Industry: It is used for the manufacture of body bodies, engine components and internal structures.
- Construction: Sheet metal is essential in the production of metal structures, roofs, facades and support systems.
- Appliances: Many products such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens contain sheet metal parts that ensure their structural integrity.
- Furniture and Decoration: Sheet metal is used in the design and manufacture of contemporary furniture, offering a modern aesthetic and great durability.
Sheet metal fabrication is a key process in industrial production that involves various techniques such as cutting, bending, and welding. Its versatility and applicability in multiple sectors make it an unavoidable material in modern manufacturing. EMS Group is dedicated to providing innovative and efficient solutions in sheet metal fabrication, ensuring high-quality products that meet the specific needs of our customers. With the right expertise and state-of-the-art technology, we are committed to taking your projects to the next level in the field of industrial manufacturing.
At EMS Group, innovation and customer satisfaction are our priority!